
t has already been narrated how, upon the arrival of the army corps from England, the greater part was drafted to Natal, while some went to the western side, and started under Lord Methuen upon the perilous enterprise of the relief of Kimberley. It has also been shown how, after three expensive victories, Lord Methuen’s force met with a paralysing reverse, and was compelled to remain inactive within twenty miles of the town which they had come to succour. Before describing how that succour did eventually arrive, some attention must be paid to the incidents which had occurred within the city.
I am directed to assure you that there is no reason for apprehending that Kimberley or any part of the colony either is, or in any contemplated event will be, in danger of attack. Mr. Schreiner is of opinion that your fears are groundless and your anticipations in the matter entirely without foundation.' Such is the official reply to the remonstrance of the inhabitants, when, with the shadow of war dark upon them, they appealed for help. It is fortunate, however, that a progressive British town has usually the capacity for doing things for itself without the intervention of officials. Kimberley was particularly lucky in being the centre of the wealthy and alert De Beers Company, which had laid in sufficient [299/300] ammunition and supplies to prevent the town from being helpless in the presence of the enemy. But the cannon were popguns, firing a 7-pound shell for a short range, and the garrison contained only seven hundred regulars, while the remainder were mostly untrained miners and artisans. Among them, however, there was a sprinkling of dangerous men from the northern wars, and all were nerved by a knowledge that the ground which they defended was essential to the Empire. Ladysmith was no more than any other strategic position, but Kimberley was unique, the centre of the richest tract of ground for its size in the whole world. Its loss would have been a heavy blow to the British cause, and an enormous encouragement to the Boers.

Cecil J. Rhodes. Mortimer Menpes. Watercolor. Click on image to enlarge it.
On October 12th, several hours after the expiration of Kruger’s ultimatum, Cecil Rhodes threw himself into Kimberley. This remarkable man, who stands for the future of South Africa as clearly as the Dopper Boer stands for its past, has, both in features and in character, some traits which may, without extravagance, be called Napoleonic. The restless energy, the fertility of resource, the attention to detail, the wide sweep of mind, the power of terse comment — all these recall the great emperor. So does the simplicity of private life in the midst of excessive wealth. And so finally does a want of scruple where an ambition is to be farthered, shown, for example, in that enormous donation to the Irish party by which he made a bid for their parliamentary support, and in the story of the Jameson raid. A certain cynicism of mind and a grim humour complete the parallel. But Rhodes is a Napoleon of peace. The consolidation of South Africa under the freest and most progressive form of government is the large object on which he has expended his energies and his fortune, but [300/301] the development of the country in every conceivable respect, from the building of a railway to the importation of a pedigree bull, engages his unremitting attention.
It was on October 15th that the fifty thousand inhabitants of Kimberley first heard the voice of war. It rose and fell in a succession of horrible screams and groans which travelled far over the veldt, and the outlying farmers marvelled at the dreadful clamour from the sirens and the hooters of the great mines. Those who have endured all — the rifle, the cannon, and the hunger — have said that those wild whoops from the sirens were what had tried their nerve the most.
The Boers in scattered bands of horsemen were thick around the town, and had blocked the railroad. They raided cattle upon the outskirts, but made no attempt to rush the defence. The garrison, who, civilian and military, approached four thousand in number, lay close in rifle pit and redoubt waiting for an attack which never came. The perimeter to be defended was about eight miles, but the heaps of tailings made admirable fortifications, and the town had none of those inconvenient heights around it which had been such bad neighbours to Ladysmith. Picturesque surroundings are not favourable to defence.
On October 24th the garrison, finding that no attack was made, determined upon a reconnaissance. The mounted force, upon which most of the work and of the loss fell, consisted of the Diamond Fields Horse, a small number of Cape Police, a company of Mounted Infantry, and a body called the Kimberley Light Horse. With two hundred and seventy volunteers from this force Major Scott-Turner, a redoubtable fighter, felt his way to the north until he came in touch with the Boers. The latter, who were much superior in numbers, [301/302] manoeuvred to cut him off, but the arrival of two companies of the North Lancashire Regiment turned the scale in our favour. We lost three killed and twenty-one wounded in the skirmish. The Boer loss is unknown, but their commander Botha was slain.

General Louis Botha one of nine portraits of Boer military leaders by F. Leiber depicted in De Aanvoerders van hut Heldhaftige Boernleger. Click on image to enlarge it.
On November 4th Commandant Wessels formally summoned the town, and it is asserted that he gave Colonel Kekewich leave to send out the women and children. That officer has been blamed for not taking advantage of the permission — or at the least for not communicating it to the civil authorities. As a matter of fact the charge rests upon a misapprehension. In Wessels’ letter a distinction is made between Africander and Enghsh women, the former being offered an asylum in his camp. This offer was made known, and half a dozen persons took advantage of it. The suggestion, however, in the case of the English carried with it no promise that they would be conveyed to Orange River, and a compliance with it would have put them as helpless hostages into the hands of the enemy. As to not publishing the message it is not usual to publish such official documents, but the offer was shown to Mr. Rhodes, who concurred in the impossibility of accepting it.
It is difficult to allude to this subject without touching upon the painful but notorious fact that there existed during the siege considerable friction between the military authorities and a section of the civilians, of whom Mr. Rhodes was chief. Among other characteristics Rhodes bears any form of restraint very badly, and chafes mightily when unable to do a thing in the exact way which he considers best. He may be a Napoleon of peace, but his warmest friends could never describe him as a Napoleon of war, for his military [302/303] forecasts have been erroneous, and the management of the Jameson fiasco certainly inspires no confidence in the judgment of any one concerned. That his intentions were of the best, and that he had the good of the Empire at heart, may be freely granted; but that these motives should lead him to cabal against, and even to threaten, the military governor, or that he should attempt to force Lord Roberts’s hand in a military operation, is most deplorable. Every credit may be given to him for all his aid to the military — he gave with a good grace what the garrison would otherwise have had to commandeer — but it is a fact that the town would have been more united, and therefore stronger, without his presence. Colonel Kekewich and his chief staff officer, Major O'Meara, were as much plagued by intrigue within as by the Boers without.

Left: General Cronjé before Kimberley, with Captain P. T. van der Merwe and his artilleryr. Source: Rompel’s Heroes of the Boer War. “Om Piet gave orders that Long Tom should attack Kimberley. Roaring and thundering the gun threw the big shells into Rhodes’s fortifications.” Click on image to enlarge it.
On November 7th the bombardment of the town commenced from nine 9-pounder guns to which the artillery of the garrison could give no adequate reply. The result, however, of a fortnight’s fire, during which seven hundred shells were discharged, was the loss of two non-combatants. The question of food was recognised as being of more importance than the enemy’s fire. An early relief appeared probable, however, as the advance of Methuen’s force was already known. One pound of bread, two ounces of sugar, and half a pound of meat were allowed per head. It was only on the small children that the scarcity of milk told with tragic effect. At Ladysmith, at Mafeking, and at Kimberley hundreds of these innocents were sacrificed.
November 25th was a red-letter day with the garrison, who made a sortie under the impression that Methuen was not far off, and that they were assisting his operations. The attack was made upon one of the Boer [303/304] positions by a force consisting of a detachment of the Light Horse and of the Cape Police, and their work was brilliantly successful. The actual storming of the redoubt was carried out by some forty men, of whom but four were killed. They brought back thirty-three prisoners as a proof of their victory, but the Boer gun, as usual, escaped us. In this brilliant affair Scott-Turner was wounded, which did not prevent him, only three days later, from leading another sortie, which was as disastrous as the first had been successful. Save under very exceptional circumstances it is in modern warfare long odds always upon the defence, and the garrison would probably have been better advised had they refrained from attacking the fortifications of their enemy — a truth which Baden-Powell learned also at Game Tree Hill. As it was, after a temporary success the British were blown back by the fierce Mauser fire, and lost the indomitable Scott-Turner, with twenty-one of his brave companions killed and twenty-eight wounded, all belonging to the colonial corps. The Empire may reflect with pride that the people in whose cause mainly they fought showed themselves by their gallantry and their devotion worthy of any sacrifice which has been made.
Again the siege settled down to a monotonous record of decreasing rations and of expectation. On December 10 there came a sign of hope from the outside world. Far on the southern horizon a little golden speck shimmered against the blue African sky. It was Methuen’s balloon gleaming in the sunshine. Next morning the low grumble of distant cannon was the sweetest of music to the listening citizens. But days passed without further news, and it was not for more than a week that they learned of the bloody repulse of Magersfontein, and that help was once more indefinitely postponed. Heliographic [304/305] communication had been opened with the relieving army, and it is on record that the first message flashed through from the south was a question about the number of a horse. With inconceivable stupidity this has been cited as an example of military levity and incapacity. Of course the object of the question was a test as to whether they were really in communication with the garrison. It must be confessed that the town seems to have contained some very querulous and unreasonable people.
The New Year found the beleaguered city reduced to a quarter of a pound of meat per head, while the health of the inhabitants began to break down under their confinement. Their interest, however, was keenly aroused by the attempt made in the De Beers workshops to build a gun which might reach their opponents. This remarkable piece of ordnance, constructed by an American named Labram by the help of tools manufactured for the purpose and of books found in the town, took the shape eventually of a 28 lb. rifled gun, which proved to be a most efficient piece of artillery. With grim humour, Mr. Rhodes’s compliments had been inscribed upon the shells — a fair retort in view of the openly expressed threat of the enemy that in case of his capture they would carry him in a cage to Pretoria.
Left: The Long Cecil, the artillery piece created by George Labram (1859-1900), the Chief Mechanical Engineer at the De Beers diamond mines in Kimberley during the siege. According to Wikipedia (source of these the image and this information) Labram, who was killed a week before the siege ended when a shell struck the Grand Hotel, also created a 155-foor watchtower, search lights, telephone system, fresh-water supply, and two armored trains. PH Parsons has made a color photo of the gun named for Cecil Rhodes.
The Boers, though held off for a time by this unexpected piece of ordnance, prepared a terrible answer to it. On February 7th an enormous gun, throwing a 96 lb. shell, opened from Kamfersdam, which is four miles from the centre of the town. The shells, following the evil precedent of the Germans in 1870, were fired not at the forts, but into the thickly populated city. Day and night these huge missiles exploded, shattering the houses and occasionally killing or maiming the occupants [305/306] Some thousands of the women and children were conveyed down the mines, where, in the electric-lighted tunnels, they lay in comfort and safety. One surprising revenge the Boers had, for by an extraordinary chance one of the few men killed by their gun was the ingenious Labram who had constructed the 28-pounder. By an even more singular chance, Leon, who was responsible for bringing the big Boer gun, was struck immediately afterwards by a long-range rifle-shot from the garrison.
The historian must be content to give a tame account of the siege of Kimberley, for the thing itself was tame. Indeed ‘siege’ is a misnomer, for it was rather an investment or a blockade. Such as it was, however, the inhabitants became very restless under it, and though there were never any prospects of surrender the utmost impatience began to be manifested at the protracted delay on the part of the relief force. It was not till later that it was understood how cunningly Kimberley had been used as a bait to hold the enemy until final preparations had been made for his destruction.
And at last the great day came. It is on record how dramatic was the meeting between the mounted outposts of the defenders and the advance guard of the relievers, whose advent seems to have been equally unexpected by friend and foe. A skirmish was in progress on February 15th between a party of the Kimberley Light Horse and of the Boers, when a new body of horsemen, unrecognised by either side, appeared upon the plain and opened fire upon the enemy. One of the strangers rode up to the patrol. ‘What the dickens does K.L.H. mean on your shoulder-strap?’ he asked. ‘It means Kimberley Light Horse. Who are you?’ ‘I am one [306/307] of the New-Zealanders.’ Macaulay in his wildest dream of the future of the much-quoted New-Zealander never pictured him as heading a rescue force for the relief of a British town in the heart of Africa.
The population had assembled to watch the mighty cloud of dust which rolled along the south-eastern horizon. What was it which swept westwards within its reddish heart? Hopeful and yet fearful they saw the huge bank draw nearer and nearer. An assault from the whole of Cronje’s army was the thought which passed through many a mind. And then the dust-cloud thinned, a mighty host of horsemen spurred out from it, and in the extended far-flung ranks the glint of spearheads and the gleam of scabbards told of the Hussars and Lancers, while denser banks on either flank marked the position of the whirling guns. Wearied and spent with a hundred miles' ride the dusty riders and the panting, dripping horses took fresh heart as they saw the broad city before them, and swept with martial rattle and jingle towards the cheering crowds. Amid shouts and tears French rode into Kimberley while his troopers encamped outside the town.
To know how this bolt was prepared and how launched, the narrative must go back to the beginning of the month. At that period Methuen and his men were still faced by Cronje and his entrenched forces, who, in spite of occasional bombardments, held their position between Kimberley and the relieving army. French, having handed over the operations at Colesberg to Clements, had gone down to Cape Town to confer with Roberts and Kitchener. Thence they all three made their way to the Modder River, which was evidently about to be the base of a more largely conceived series of operations than any which had yet been undertaken. [307/308]
In order to draw the Boer attention away from the thunderbolt which was about to fall upon their left flank, a strong demonstration ending in a brisk action was made early in February upon the extreme right of Cronje’s position.

General Hector Macdonald. Mortimer Menpes. Watercolor. Click on image to enlarge it.
The force, consisting of the Highland Brigade, two squadrons of the 9th Lancers, and the 62nd Battery, was under the command of the famous Hector Macdonald. ‘Fighting Mac’ as he was called by his men, had joined his regiment as a private, and had worked through the grades of corporal, sergeant, captain, major, and colonel, until now, still in the prime of his manhood, he found himself riding at the head of a brigade. A bony, craggy Aberdonian, with a square fighting head and a bulldog jaw, he had conquered the exclusiveness and routine of the British service by the same dogged qualities which made him formidable to Dervish and to Boer. With a cool brain, a steady nerve, and a proud heart, he is an ideal leader of infantry, and those who saw him manoeuvre his brigade in the crisis of the battle of Omdurman speak of it as the one great memory which they carried back from the engagement. On the field of battle he turns to the speech of his childhood, the jagged, rasping, homely words which brace the nerves of the northern soldier. This was the man who had come from India to take the place of poor Wauchope, and to put fresh heart into the gallant but sorely stricken brigade.
The four regiments which composed the infantry of the force — the Black Watch, the Argyll and Sutherlands, the Seaforths, and the Highland Light Infantry — left Lord Methuen’s camp on Saturday, February 3rd, and halted at Fraser’s Drift, passing on next day to Koodoosberg. The day was very hot, and the going very heavy, and many men fell out, some never to return. The [308/309] drift (or ford) was found, however, to be undefended, and was seized by Macdonald, who established himself strongly among the kopjes on the south bank. A few Boer scouts were seen hurrying with the news of his coming to the head laager.

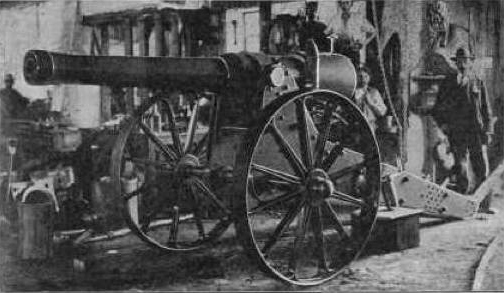
The 155 mm. Creusot Long Tom manufacured by Schbeider et Cie in Creusot, France. In this photograph the gun is being transported to the Siege of Kimberly. Click on image to enlarge it.
The effect of these messages was evident by Tuesday February 6th), when the Boers were seen to be assembling upon the north bank. By next morning they were there m considerable numbers, and began an attack upon a crest held by the Seaforths. Macdonald threw two companies of the Black Watch and two of the Highland Light Infantry into the fight. The Boers made excellent practice with a 7-pounder mountain gun, and their rifle fire, considermg the good cover which our men had, was very deadly. Poor Tait, of the Black Watch, good portsman and gallant soldier, with one wound hardly healed upon his person, was hit again. ‘They've got me his time’; were his dying words. Blair, of the Seaforths, had his carotid cut by a shrapnel bullet, and lay for hours while the men of his company took turns to squeeze the artery. But our artillery silenced the Boer gun, and our infantry easily held their riflemen. Babington with the cavalry brigade arrived from the camp about 1.30 moving along the north bank of the river. In spite of the fact that men and horses were weary from a tiring march it was hoped by Macdonald’s force that they would work round the Boers and make an attempt capture either them or their gun. But the horsemen seem not to have realised the position of the parties, or the possibility of bringing off a considerable coup, so that the action came to a tame conclusion, the Boers retiring. unpursued from their attack. On Thursday, February 8th they were found to have withdrawn, and on the same evening our own force was recalled, to the surprise and disappointment [309/310] of the public at home, who had not realised that in directing their attention to their right flank the column had already produced the effect upon the enemy for which they had been sent. They could not be left there, as they were needed for those great operations which were pending. It was on the 9th that the brigade returned; on the 10th they were congratulated by Lord Roberts in person; and on the 11th those new dispositions were made which were destined not only to relieve Kimberley, but to inflict a blow upon the Boer cause from which it was never able to recover.


Two watercolor portraits of Lord Roberts by Mortimer Menpes. Click on images to enlarge them.
Small, brown, and wrinkled, with puckered eyes and alert manner, Lord Roberts in spite of his sixty-seven years preserves the figure and energy of youth. The active open-air life of India keeps men fit for the saddle when in England they would only sit their club armchairs, and it is hard for any one who sees the wiry figure and brisk step of Lord Roberts to realise that he has spent forty -one years of soldiering in what used to be regarded as an unhealthy climate. He had carried into late life the habit of martial exercise, and a Russian traveller has left it on record that the sight which surprised him most in India was to see the veteran commander of the army ride forth with his spear and carry off the peg with the skill of a practised trooper. In his early youth he had shown in the Mutiny that he possessed the fighting energy of the soldier to a remarkable degree, but it was only in the Afghan War of 1880 that he had an opportunity of proving that he had rarer and more valuable gifts, the power of swift resolution and determined execution. At the crisis of the war he and his army disappeared entirely from the public ken only to emerge dramatically as victors at a point three hundred miles distant from where they had vanished. [310/311]
It is not only as a soldier, but as a man, that Lord Roberts possesses some remarkable characteristics. He has in a supreme degree that magnetic quality which draws not merely the respect but the love of those who know him. In Chaucer’s phrase, he is a very perfect gentle knight. Soldiers and regimental officers have for him a feeling of personal affection such as the unemotional British Army has never had for any leader in the course of our history. His chivalrous courtesy, his unerring tact, his kindly nature, his unselfish and untiring devotion to their interests have all endeared him to those rough loyal natures, who would follow him with as much confidence and devotion as the grognards of the Guard had in the case of the Great Emperor. There were some who feared that in Roberts’s case, as in so many more, the donga and kopje of South Africa might form the grave and headstone of a military reputation, but far from this being so he has consistently shown a wide sweep of strategy and a power of conceiving the effect of scattered movements over a great extent of country which have surprised his warmest admirers. In the second week of February his dispositions were ready, and there followed the swift series of blows which brought the Boers upon their knees and the war eventually to a termination. Of these we shall only describe here the exploits of the fine force of cavalry which, after a ride of a hundred miles, broke out of the heart of that reddish dust-cloud and swept the Boer besiegers away from hard-pressed Kimberley.
In order to strike unexpectedly, Lord Roberts had not only made a strong demonstration at Koodoosdrift, at the other end of the Boer line, but he had withdrawn his main force some forty miles south, taking them down by rail to Belmont and Enslin with such secrecy [311/312] that even commanding officers had no idea whither the troops were going. The cavalry which had come from French’s command at Colesberg had already reached the rendezvous, travelling by road to Naauwpoort, and thence by train. This force consisted of the Carabineers, New South Wales Lancers, Inniskilhngs, composite regiment of Household Cavalry, 10th Hussars, with some mounted infantry and two batteries of Horse Artillery, making a force of nearly three thousand sabres. To this were added the 9th and 12th Lancers from Modder River, the 16th Lancers from India, the Scots Greys, which had been patrolling Orange River from the beginning of the war, Rimington’s Scouts, and two brigades of mounted infantry under Colonels Ridley and Hannay. Five other batteries of Horse Artillery were added to the force, making seven in all, with a pontoon section of Royal Engineers. The total number of men was about five thousand. By the night of Sunday, February 11th, this formidable force had concentrated at Ramdam, twenty miles north-east of Belmont, and was ready to advance. At two in the morning of Monday, February 12th, the start was made, and the long sinuous line of night-riders moved off over the shadowy veldt, the beat of twenty thousand hoofs, the clank of steel, and the rumble of gun-wheels and tumbrils swelling into a deep low roar like the surge upon the shingle.

Crossing the Modder. Mortimer Menpes. 1901. Watercolor. Click on image to enlarge it.
Two rivers, the Riet and the Modder, intervened between French and Kimberley. By daylight on the 12th the head of his force had reached Waterval Drift, which was found to be defended by a body of Boers with a gun. Leaving a small detachment to hold them, French passed his men over Dekiel’s Drift, higher up the stream, and swept the enemy out of his [312/313] position.1 At the cost of a very small loss he held both sides of the ford, but it was not until midnight that the whole long column was brought across, and bivouacked upon the northern bank. In the morning the strength of the force was enormously increased by the arrival of one more horseman. It was Roberts himself, who had ridden over to give the men a send-off, and the sight of his wiry erect figure and mahogany face sent them full of fire and confidence upon their way.
But the march of this second day (February 13th) was a military operation of some difficulty. Thirty long waterless miles had to be done before they could reach the Modder, and it was possible that even then they might have to fight an action before winning the drift. The weather was very hot, and through the long day the sun beat down from an unclouded sky, while the soldiers were only shaded by the dust-bank in which they rode. A broad arid plain, swelling into stony hills, surrounded them on every side. Here and there in the extreme distance, mounted figures moved over the vast expanse — Boer scouts who marked in amazement the advance of this great array. Once or twice these men gathered together, and a sputter of rifle fire broke out upon our left flank, but the great tide swept on and carried them with it. Often in this desolate land the herds of mottled springbok and of grey rekbok could be seen sweeping over the plain, or stopping with that curiosity upon which the hunter trades, to stare at the unwonted spectacle.
So all day they rode, hussars, dragoons, and lancers, over the withered veldt, until men and horses drooped [313/314] with the heat and the exertion. A front of nearly two miles was kept, the regiments moving two abreast in open order; and the sight of this magnificent cloud of horsemen sweeping over the great barren plain was a glorious one. The veldt had caught fire upon the right, and a black cloud of smoke with a lurid heart to it covered the flank. The beat of the sun from above and the swelter of dust from below were overpowering. Gun horses fell in the traces and died of pure exhaustion. The men, parched and silent, but cheerful, strained their eyes to pierce the continual mirage which played over the horizon, and to catch the first glimpse of the Modder. At last, as the sun began to slope down to the west, a thin line of green was discerned, the bushes which skirt the banks of that ill-favoured stream. With renewed heart the cavalry pushed on and made for the drift, while Major Rimington, to whom the onerous duty of guiding the force had been entrusted, gave a sigh of relief as he saw that he had indeed struck the very point at which he had aimed.
The essential thing in the movements had been speed — to reach each point before the enemy could concentrate to oppose them. Upon this it depended whether they would find five hundred or five thousand waiting on the further bank. It must have been with anxious eyes that French watched his first regiment ride down to Klip Drift. If the Boers should have had notice of his coming and have transferred some of their 40-pounders, he might lose heavily before he forced the stream. But this time, at last, he had completely outmanoeuvred them. He came with the news of his coming, and Broadwood with the 12th Lancers rushed the drift. The small Boer force saved itself by flight, and the camp, the wagons, and the supplies remained [314/315[ with the victors. On the night of the 13th he had secured the passage of the Modder, and up to the early morning the horses and the guns were splashing through its coffee-coloured waters.
French’s force had now come level to the main position of the Boers, but had struck it upon the extreme left wing. The extreme right wing, thanks to the Koodoosdrift demonstration, was fifty miles off, and this line was naturally very thinly held, save only at the central position of Magersfontein. Cronje could not denude this central position, for he saw Methuen still waithig in front of him, and in any case Klip Drift is twenty-five miles from Magersfontein. But the Boer left wing, though scattered, gathered into some sort of cohesion on Wednesday (February 14th), and made an effort to check the victorious progress of the cavalry. It was necessary on this day to rest at Klip Drift, until Kelly-Kenny should come up with the infantry to hold what had been gained. All day the small bodies of Boers came riding in and taking up positions between the column and its objective.
Next morning the advance was resumed, the column being still forty miles from Kimberley with the enemy in unknown force between. Some four miles out French came upon their position, two hills with a long low nek between, from which came a brisk rifle fire supported by artillery. But French was not only not to be stopped, but could not even be retarded. Disregarding the Boer fire completely the cavalry swept in wave after wave over the low nek, and so round the base of the hills. The Boer riflemen upon the kopjes must have seen a magnificent military spectacle as regiment after regiment, the 9th Lancers leading, all in very open order, swept across the plain at a gallop, and so passed over the nek. [315/316]
A few score horses and half as many men were left behind them, but forty or fifty Boers were cut down in the pursuit. It appears to have been one of the very few occasions during the campaign when that obsolete and absurd weapon the sword was anything but a dead weight to its bearer.
And now the force had a straight run in before it, for it had outpaced any further force of Boers which may have been advancing from the direction of Magersfontein. The horses, which had come a hundred miles in four days with insufficient food and water, were so done that it was no uncommon sight to see the trooper not only walking to ease his horse, but carrying part of his monstrous weight of saddle gear. But in spite of fatigue the force pressed on until in the afternoon a distant view was seen, across the reddish plain, of the brick houses and corrugated roofs of Kimberley. The Boer besiegers cleared off in front of it, and that night (February 15th) the relieving column camped on the plain two miles away, while French and his staff rode in to the rescued city.
The war has been a cruel one for the cavalry, who have been handicapped throughout by the nature of the country and by the tactics of the enemy. They are certainly the branch of the service which has had least opportunity for distinction. The work of scouting and patrolling is the most dangerous which a soldier can undertake, and yet from its very nature it can find no chronicler. The war correspondent, like Providence, is always with the big battalions, and there never was a campaign in which there was more unrecorded heroism, the heroism of the picket and of the vedette which finds its way into no newspaper paragraph. But in the larger operations of the war it is difficult to say that [316/317] cavalry, as cavalry, have justified their existence. In the opinion of many the tendency of the future will be to convert the whole force into mounted infantry. How little is required to turn our troopers into excellent foot soldiers was shown at Magersfontein, where the 12th Lancers, dismounted by the command of their colonel, Lord Airlie, held back the threatened flank attack all morning. A little training in taking cover, leggings instead of boots, and a rifle instead of a carbine would give us a formidable force of twenty thousand men who could do all that our cavalry does, and a great deal more besides. It is undoubtedly possible on many occasions in this war, at Colesberg, at Diamond Hill, to say * Here our cavalry did well.' They are brave men on good horses, and they may be expected to do well. But the champion of the cavalry cause must point out the occasions where the cavalry did something which could not have been done by the same number of equally brave and equally well-mounted infantry. Only then will the existence of the cavalry be justified. The lesson both of the South African and of the American civil war is that the light horseman who is trained to fight on foot is the type of the future.
A few more words as a sequel to this short sketch of the siege and relief of Kimberley. Considerable surprise has been expressed that the great gun at Kamfersdam, a piece which must have weighed many tons and could not have been moved by bullock teams at a rate of more than two or three miles an hour, should have eluded our cavalry. It is indeed a surprising circumstance, and yet it was due to no inertia on the part of our leaders, but rather to one of the finest examples of Boer tenacity in the whole courBe of the war. The instant [317/318] that Kekewich was sure of relief he mustered every available man and sent him out to endeavour to get the gun. It had already been removed, and its retreat was covered by the strong position of Dronfield, which was held both by riflemen and by light artillery. Finding himself unable to force it, Murray, the commander of the detachment, remained in front of it. Next morning (Friday) at three o'clock the weary men and horses of two of French’s brigades were afoot with the same object. But still the Boers were obstinately holding on to Dronfield, and still their position was too strong to force, and too extended to get round with exhausted horses. It was not until the night after that the Boers abandoned their excellent rearguard action, leaving one light gun in the hands of the Cape Police, but having gained such a start for their heavy one that French, who had other and more important objects in view, could not attempt to follow it.
Last modified 18 December 2013